Perceptron Algorithm and Backpropagation with Iris Flower Data
Introduction
The Iris Data Set includes the width and length of both petal and sepal of 150 flowers. The measurements were obtained from 50 flowers from three iris varieties: iris setosa; iris versicolor; and iris virginica. The iris data set is a list of these measurements labelled with the variety of the flower from which the measurement were taken.
Objectives
Clearly it is interesting to see if we can train a neural network to classify iris varieties. Given sepal and petal lengths and widths, build a neural network to establish the iris variety, like iris classification. First, investigate whether a perceptron network can classify iris variety, provide own implementation of the perceptron algorithm. Then, implement the backpropagation algorithm to investigate if and how this network is superior to the perceptron network.
Question
- Make a scatter plot of petal length against petal width. This means that for each entry in the data set you plot a point in the 2D plane with petal length as y coordinate, and petal width as x coordinate. Use three different markers (or different colours), one for setosa, one for versicolor and one for virginica. Plot other sepal/petal length/width combinations as well.
- Based on the plots, do you believe that setosa vs. non-setosa can be learnt by a perceptron? That is, given a perceptron with 4 inputs, for petal length, petal width sepal length, and sepal width, can you find four weights and a bias which can classify setosa vs. non-setosa? Explain your answer. If you can, give these weights and bias. Draw the decision line of your perceptron on the plots of the last question.
- Implement the standard perceptron algorithm without learning rate and train a perceptron for the setosa vs. non-setosa classification problem. Do you expect the algorithm to converge? Explain why! Does the algorithm converge? Is the output correct? If it does not converge, now introduce a learning rate, and use a sensible stopping criterion. Report the learning rate, stopping criterion and argue whether the result you obtain is in line with what you know the algorithm is capable of. The same questions about virginica vs. non-virginica? versicolor vs non-versicolor? There is a major difference between versicolor and the other two. Explain the difference using the plots you made.
- Using your earlier results, build a neural network with four inputs and three outputs. The network should produce the following desired classification: versicolor = (1, 0, 0), setosa = (0,1,0), virginica = (0,0,1). Do not use backpropagation. Combine the classifiers you have developed so far with some elementary logic - which you should implement using artificial neurons! Create a working program that implements your network. Your program must compile and run. Upon running, it must ask for 4 numbers: PL PW, SL, SW and produce a classification. In the report, explain the strategy you used, draw the full network and give all weights and biases. Evaluate the accuracy of your network.
-
A tutorial will demonstrate an application of the Keras framework to solve the XOR problem. This implementation will be made available to you. You will then adapt this implementation for use on the iris data set.
Apply your implementation in a program that can classify the iris data. Create a demo program that can take 4 numbers PL PW, SL, SW and produce a classification. Evaluate the performance of your algorithm. Explain whether it is better or worse than the network you built in question 4. Give two reasons why your network cannot achieve perfect classification.
Experiment with the number of hidden nodes. Consider experimenting with the loss function. Make sure you create a training data set, and not to evaluate your network on this training data set.
Implementation
1. Scatter Plot
At first, I need to do data pre-processing. Add a header to iris.data because it is more easily to do classification.
To plot a scatter of sepal/petal length/width combinations, there will have 12 differenct combinations. Use Matplotlib can help me solve this problem. The plot as shown below: (blue = setosa, green = versicolor, red = virginica)

2. Decision Line
Decision line also can be named Decision boundary. Look at the figure above, the blue points are clearly separated from the other two colors in each subplot. Thus, I can draw a straight line to separate the points of the setosa from the colors of the other two classes in each subplot. It means the setosa is linearly separated from the non-setosa class.
The classes can be learnt by a perceptron or not is depend on whether it can be separated linearly. Therefore, the setosa vs. non-setosa can be learnt by a perceptron.
For example, I can give sample weights and bias. I draw it in a 2D plot, the horizontal coordinate is petal width and the vertical coordinate is petal length. The figure are shown below:

In this figure, these four weights and a bias are .
3. Simple Perceptron
I need to implement a simple perceptron algorithm with or without a learning rate and train it for the setosa vs. non-setosa, virginica vs. non-virginica and versicolor vs. non-versicolor, respectively.
4. Neural Network
I need to build a simple neural network with four inputs (sepal length, sepal width, petal length, petal width) and three outputs (setosa, versicolor, virginica). The network should produce the following desired classification: versicolor = (1, 0, 0), setosa = (0, 1, 0), virginica = (0, 0, 1).
By looking at the outputs I expect to get, when the setosa and virginica output 0, the versicolor will output 1. This is a NOR gate which means I can use setosa and virginica to replace the output of versicolor. So, I can only use two classes, setosa and virginica, in the hidden layer without versicolor. Specifically, due to I define that when input 0, it will output for 0, and when input 0, it will output for 1. Hence, I set setosa and virginica both output -1, and set bias 0.5 to make virginica output 1 at the end. The sub-neural network of versicolor as shown below:

In addition, when the setosa get input 1, it will output 1 as well. And the virginica is same. These sub-neural network show as following:


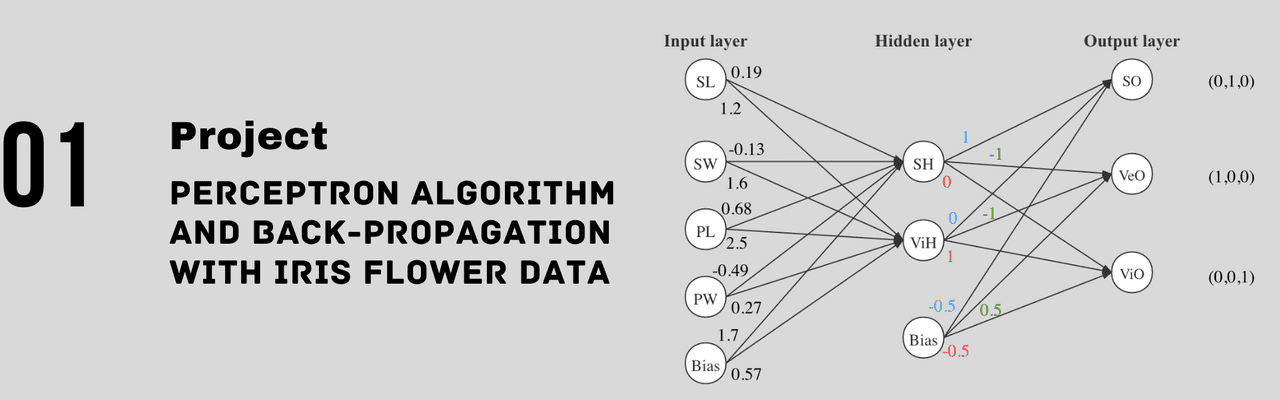
As for whole network, I would make 4 parameters: PL, PW, SL, SW as the input layer of this neural network. I decide to use np.random.randn() to get 4 weights and a bias randomly with standard normal distribution. Then, the hidden layer as I mentioned above, so the full network work is below:

I run this neural network serval times to get a average accuracy: , and there are an average of 5 misclassified points per run.
5. Keras Model
The last requirement make me use Keras to build a model, solving this XOR problem. Compared to AND and OR problems, XOR problems is inseparable (cannot find only one line to achieve linear separation), as shown below.

As we know, perceptron is a linear classification model that cannot deal with non-linear separation problem. So, I need to use Keras to build network to solve this problem.
This model built by Keras includes a input layer, a hidden layer (4 nodes at first experiment) and an output layer (including 3 nodes which represent label predictions). I decide to use ReLU as the hidden layer activation and softmax for the output layer activation. The optimization function is SGD with learning rate 0.01 and momentum 0.9. The full network model is as follows:


The plot of loss and accuracy as shown below:

According to this plot above, it is clear that the curves have converged after 200 epochs. In addition, the accuracy is high as (even more than ), and the accuracy of the test data set (30 data) is , which means this model by Keras is excellent. So, it is clear that this model has better performance that the network I built in Q4.
There are some reasons can explain it:
- The network I built does not use backpropagation but Keras does.
- The Keras use advanced activation, optimizier and loss function.
Source code
The source code of this project can be viewed at Perceptron.
